Specialized TCP/IP protocols, popularly known as SMTP and IMAP, are used for sending and receiving emails. Understanding the difference between SMTP vs IMAP is crucial for developers to satisfy the demands of contemporary applications.
To make it easily understandable, we will discuss SMTP and IMAP protocols, their main differences, and the email communication process.
So, without any delay, let’s get started!
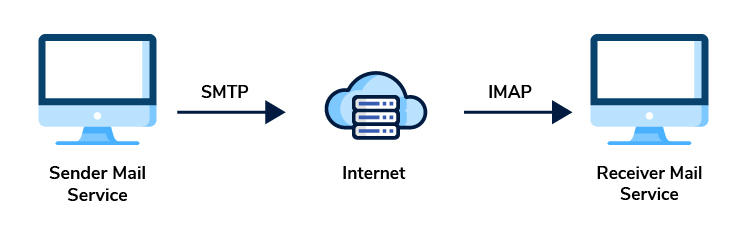
How Does Email Communication Work?
The email communication flow involves three key parties:
- Sender: The individual who initiates the email.
- Recipient: The individuals who receive the email.
- Mail server: The intermediary entity responsible for receiving and routing the email.
When a sender sends an email, it is directed to the server. The email server facilitates the delivery of the email to the intended recipient. Once connectivity is established, the email protocol plays a crucial role as it defines the standards for communication.
What is Protocol in Email Communication?
A protocol in email communication is a set of rules that ensures the proper transmission of emails over the Internet. Email protocols allow different machines, networks, and operating systems to exchange and manage emails using various email programs and devices. These protocols also define the roles and functions of the email clients and servers involved in sending and receiving emails.
Some widely used communication protocols include TCP/IP, User Datagram Protocol (UDP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
In the context of email communication, the following three primary protocols are extensively employed and supported by most browsers.
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Post Office Protocol (POP)
Each of these protocols has a specific purpose and mechanism for handling emails. Users can choose to use either SMTP or IMAP or a combination of both, depending on their email service provider and email client. POP3 is an older protocol that is largely replaced by IMAP.
What is SMTP and How Does it Work?
SMTP, an acronym for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is the widely accepted email transmission industry standard.
You can effectively send, relay, or forward messages from a mail client (such as Microsoft Outlook) to a receiving email server when utilizing SMTP. In this process, a sender employs an SMTP server to facilitate the transmission of an email message.
When considering the choice between SMTP and IMAP, it is crucial to understand that SMTP primarily focuses on sending emails. Therefore, if you want to use email-sending functionality within your application, SMTP should be your go-to option.
Features of SMTP
- Used for relaying emails.
- SMTP aids various communication methods. For instance, it enables you to send videos, audio, and other media files with a single email to multiple clients.
- An outstanding feature of SMTP is that it can handle errors. SMTP successfully responds to various error requests by taking important actions.
- SMTP offers specific conditions for email forwarding.
- You can configure SMTP servers as email gateways.
What is IMAP and How Does it Work?
IMAP (Internet Access Message Protocol) is an email protocol primarily focused on managing and retrieving email messages from the receiving server. Unlike SMTP, which is primarily concerned with sending emails, IMAP does not facilitate email sending. Its purpose is solely to fetch messages from the email server and put it in the recipient’s inbox.
Features of IMAP
- IMAP offers the advantage of accessing emails across multiple devices, allowing for convenient mailbox organization and retrieval after logging in.
- With IMAP, you can download multiple media files easily, although the complete message cannot be downloaded without opening it first. This feature is particularly beneficial for efficient startup processes.
- IMAP is well-suited for accessing emails from various locations and managing mailboxes with multiple users.
- IMAP provides flags to track viewed messages that help in message management.
- Additionally, IMAP can decide whether to retrieve emails from the mail server before downloading them.
- Downloading multiple attached media files is simple with IMAP.
Email Automation and SMTP
When utilizing email for work purposes, you likely employ some form of email automation. For example, you may utilize marketing automation tools such as MailChimp, FreshMail, or GetResponse to send marketing emails or newsletters.
It is important to distinguish between email marketing tools and sales email automation tools in relation to SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), which determines how your emails are sent. Understanding this distinction is crucial in selecting the appropriate tool for specific types of email campaigns.
How SMTP and IMAP Work Together
Whether you need to send a transactional mail, such as a password reset, or you have to receive a notification for a paycheck, there is a probability that you are using IMAP and SMTP together.
Once you compose and send an email, your chosen email client (such as Gmail, Outlook, etc.) utilizes SMTP to deliver your message from your client to an email server.
Subsequently, the email server employs SMTP to transfer the message to the recipient’s receiving email server.
Once the recipient’s email server successfully receives the SMTP transmission (confirmed by a 250 OK response code), the recipient’s email client fetches the message through IMAP and deposits it in the inbox for the recipient’s access.
Difference Between SMTP and IMAP
Here are a few key differences between SMTP and IMAP:
| SMTP | IMAP |
| • Stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | • Stands for Internet Message Access Protocol |
| • The purpose of SMTP is to send emails from a client to a server or from one server to another. | • It is used for accessing and managing emails on a server. |
| • It operates between servers or between a client and a server. | • On the other hand, IMAP only operates between a client and a server. |
| • SMTP uses port numbers 25, 465, or 587 with TLS encryption. | • For a secure connection, IMAP uses 143 or 993 ports with SSL/TLS encryption. |
| • It allows sending, relaying, or forwarding messages. | • It only allows downloading, syncing, or processing messages. |
| • It does not store or retrieve messages on the server. | • Keeps messages on the server until deleted by the user |
| • SMTP Does not support multiple devices (browsers, email clients, etc.) and synchronization (i.e., read, unread, or flagged). | • IMAP supports multiple devices (browsers, email clients, etc.) and synchronization (i.e., read, unread, or flagged). |
Wrap Up
It’s important to know the differences between SMTP and IMAP to manage email conversations. IMAP manages new messages and ensures they are the same on all devices, while SMTP is used to send emails. SMTP ensures emails get sent reliably, and IMAP makes viewing emails from multiple devices easy. Understanding these differences can improve your email protocols, improving their email experience and making communication more efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is SMTP the same as IMAP?
No, IMAP and SMTP are not the same thing. They are two different protocols that serve different purposes in email communication. IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol, and it is used to access (retrieve) and manage emails on a mail server. On the other hand, SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, and it is used to send emails from a mail client to a mail server or from one mail server to another.
How do I find my SMTP and IMAP settings?
To find your SMTP and IMAP settings, you need to contact your email service provider or check their website for the information. Different email providers may have different settings for their SMTP and IMAP servers, such as server name, port number, encryption method, username, and password.
Can I use SMTP to receive email?
No, you cannot use SMTP to receive email. SMTP is only for sending email, not for receiving it. To receive email, you need to use another protocol, such as POP or IMAP, which allows you to download or sync your emails from the mail server to your mail client.
Is an SMTP server incoming or outgoing?
An SMTP server is outgoing, not incoming. An SMTP server is responsible for delivering emails from the sender to the recipient’s mail server. It does not store or retrieve emails on the server. An incoming server is either a POP or an IMAP server, which allows users to access their emails on the server.
Is SMTP only for Gmail?
No, SMTP is not only for Gmail. SMTP is a universal protocol that many email providers and applications use to send emails over the Internet. Gmail is one email provider that uses SMTP as its outgoing server, but it is not the only one. Other email providers, such as Outlook, Yahoo, Zoho, etc., also use SMTP as their outgoing server.



