You might be wondering what’s the difference between DMARC vs DKIM? and why you need them for better email deliverability. This is what we are going to answer in today’s article.

Email is one of the most widely used and essential forms of communication in the digital world. However, it is also one of the most vulnerable to cyberattacks, such as phishing, spoofing, and spamming.
To protect your email from these threats, you need to implement some email authentication methods that can verify the identity and integrity of your email sender and content. Two of the most popular and effective email domain authentication methods are DMARC and DKIM.
Throughout this article, we will explain everything you need to know about DMARC and DKIM and how to set up and check them for your domain.
So, without any further delay. Let’s get started!
Key Technical Terminologies You Should Know:
Before we dive in, let’s define a few technical terms in advance to prevent confusion when we get started.
- SPF Record: SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework. It’s a DNS TXT record for specifying which IP addresses are permitted to send email on behalf of your domain. Thus, you can prevent spammers from forging your domain in the “From” address of their email messages.
- Public Key Cryptography: Public key cryptography is a method of encrypting or signing data with two different keys: a public key and a private key. It’s okay to share the public key with anyone, but the private key has to remain private.
- TXT Record: It’s a type of DNS record that allows you to store arbitrary text information associated with your domain as domain metadata within your DNS Zone. In email authentication, we create DNS TXT records for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- DNS: DNS is short for Domain Name System. It’s a system that looks up and translates domain names (such as example.com) into IP addresses (such as 93.184.216.34). DNS also stores other types of information about domains, such as their mail servers, name servers, or TXT records.
What is DMARC and How Does it Work?
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. This email authentication protocol leverages SPF and DKIM to validate your email messages and allows you to get reports from the recipient’s email server.
DMARC works by adding a DMARC policy to your domain’s DNS as a TXT record. The DMARC policy instructs the receiving email servers how to handle email messages that claim to come from your domain based on the results of SPF and DKIM checks.
In a DMARC record, there are two distinct functions: reporting and enforcement.
- Enforcement specifies in your DMARC policy that if an email message fails both SPF and DKIM checks, it should be rejected or quarantined (moved to the spam folder).
- While reporting, request the receiving servers to send you reports on the DMARC results so you can monitor and improve your email authentication performance.
Using proper DMARC policy, you can protect your domain from email spoofing, phishing, and spamming, as well as improve your email deliverability, reputation, and trustworthiness.
What is DMARC syntax?
The DMARC syntax comprises a series of tags and values separated by semicolons. Each tag represents a specific parameter or option that defines how your DMARC policy works.
Let’s look at the tags that make up a DMARC record one by one, explaining the role of each tag as we go. After briefly touching on each tag, we’ll pull them all together to build a complete example of DMARC policy.
| Tag | Meaning | Value |
| v | Version | The version of the DMARC protocol. Must be “DMARC1”. |
| p | Policy | Action to take when email messages fail DMARC checks. It can be “none,” “quarantine,” or “reject.” |
| sp | Subdomain Policy | The same policy as above, but for subdomains, and if you don’t specify, the default will be the same value as p. |
| pct | Percentage | The percentage of emails that are subject to the DMARC policy. You can put any number between 0 and 100. If not specified, the default is 100. |
| rua & ruf | Reporting URI for aggregate and forensic reports | The email address or URI to get aggregate and forensic reports, respectively. You can put multiple addresses or URIs separated by commas. Must use the mailto: scheme for email addresses. |
| adkim and aspf | Alignment mode for DKIM and SPF | This specifies the method for matching the domain in the DKIM signature and SPF check, respectively, to the From header field. The value can be “r” for relaxed or “s” for strict. If you don’t specify, it defaults to “r.” |
An example of a complete DMARC policy using the above tags and values is:
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; sp=reject; pct=50; rua=mailto:dmarc@example.com; ruf=mailto:dmarc@example.com; adkim=s; aspf=s
This DMARC policy (v=DMARC1) instructs email receivers to quarantine (move to the spam folder) 50% of failing messages (p=quarantine), reject (bounce back) 50% of emails from subdomains (sp=reject), and report results to “dmarc@example.com.” It enforces strict alignment (adkim=s, aspf=s) on the DKIM and SPF authentication mechanisms for better email security.
How to Check DMARC for Your Domain
To check the DMARC record for your domain, you can use online tools such as MxTOOLBOX or EASYDMARC to perform a DNS lookup for the domain. You only need to enter the domain name and select the DMARC Lookup or Check DMARC button.
What is DKIM and How Does it Work?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) uses public key cryptography to verify the authenticity and integrity of your email content.
In DKIM, administrators have two keys:
- Private key that the email server uses to sign all emails cryptographically
- Public key, which the recipient server uses to check against the real private key of the domain.
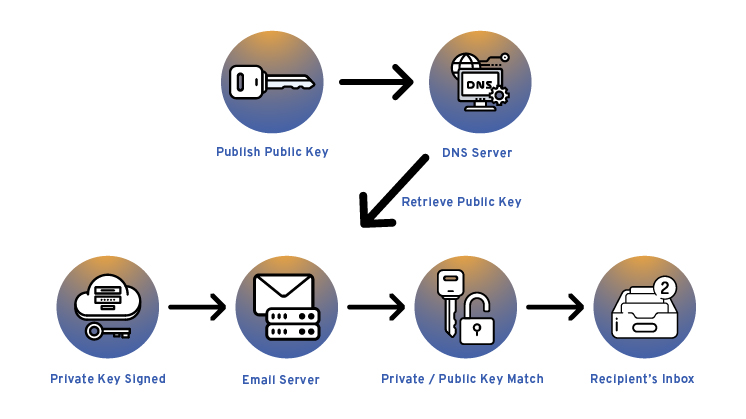
DKIM uses your domain’s private key to add a digital signature to your email header. The receiving email servers can then use your domain’s public key, which is published in your domain’s DNS as a TXT record, to validate the digital signature and check if the email content has been tampered with or not.
With DKIM, you can prove that your email content is original and unaltered, as well as prevent spammers from forging your domain in the “From” address of their email messages.
What is the syntax of DKIM records?
DKIM syntax is the format and structure of the DKIM signature in the email header and the DKIM record that you add to your domain’s DNS as a TXT record. Your DKIM TXT record contains your domain’s public key, which the receiving server uses to validate your email.
The following table shows all the tags and values that define how your DKIM record works.
| Tag | Meaning | Value |
| v | Version | The version of the DKIM protocol. Must be “DKIM1”. |
| k | Key Type | DKIM currently uses RSA as the key algorithm for the Public Key, so you can set the value as “rsa.” |
| p | Public key data | The public key data is encrypted in Base64 format. |
| h | Hash algorithm | The DKIM signature’s hash algorithm is either “sha256” or “sha1”. If not specified, it defaults to “sha256”. |
| s | Service Type / DKIM Selector | Using this selector, the receiving server should look up the DNS record |
| t | Flags | They can modify the behavior of the DKIM record. For testing, you can use “y” and “s” to indicate strictness. If you don’t specify, it defaults to none. |
Below is a sample DKIM record using all the above tags and values:
v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCdG4i8S1frT8uZCkIa0t9T6Z+7PM5YhN4kC7sFJ45PcPss61O4iTvMQLlaXddEIrjG7zGDQaLgYQgEwIp4r8cWRq5gFvHo0s5nvc7eRN3xJsETZixwp8CuxQIDIZAgkWnMwW12ZjLUTLZVEqyCJ1l1dUTf7+SMwIDAQAB; h=sha256; s=email; t=y
This DKIM record (v=DKIM1) specifies the use of RSA encryption (k=rsa) and provides a public key (p) used to verify the digital signatures of email messages. The “h=sha256” indicates the use of the SHA-256 hash algorithm for message signing. “s=email” defines the DKIM selector for this record, which tells the receiving server where to look for the DNS record. The “t=y” indicates that this DKIM record is for testing.
How to Check DKIM Record for Your Domain
For the DKIM record, you can use any domain lookup tool such as DNSCHECKER, to check the DKIM record for your domain.
To do this, you need to enter the DKIM Selector and your domain address. An “s=” tag in your DKIM signature header indicates the DKIM selector for your domain.
Let Our Experts Set Up DMARC and DKIM for You!
As we know, setting up DMARC and DKIM can be a complex and time-consuming process, especially if you are not familiar with the technical aspects of email authentication.
That’s why we offer a professional service to set up DMARC, DKIM, and SPF records for you so you can enjoy the benefits of email authentication without the hassle of doing it yourself. Our support expert will:
- Generate a DKIM key pair for your domain
- Add the DKIM record to your domain’s DNS
- Configure your email server or service to use the DKIM key pair and selector
- Add the DMARC record to your domain’s DNS
- Add and Merge all SPF records for your domain
- Test and monitor your DMARC, DKIM, SPF settings, and much more.
All you need to do is click here, fill out the form, and provide us with basic information about your domain and email server or service. We will take care of the rest! So, don’t wait any longer. Contact us today, and let us set up DMARC, DKIM, and SPF records for you!
Final Remarks
Understanding the difference between DMARC vs DKIM is necessary as these are two of the most powerful and effective email authentication methods that can help you secure your email, improve your deliverability, and protect your recipients from malicious attacks.
By setting up DMARC and DKIM for your domain, you can:
- Prove that your email sender and content are authentic and unaltered
- Prevent spammers from forging your domain in their email messages
- Specify how the receiving email servers should handle email messages that fail DMARC checks
- Receive reports on your DMARC results and performance
- Enhance your email security, reliability, and credibility
We hope that this article has given you a clear and comprehensive overview of DMARC and DKIM and how they differ from each other. If you have any difficulty setting up DMARC and DKIM yourself, just contact us and let our experts set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for you.
Thank you for reading this article!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of DKIM and DMARC?
DKIM and DMARC are email authentication methods that have several advantages, such as:
● They verify the authenticity of email senders and content.
● Prevent domain forgery by spammers.
● Specify how receiving servers handle failed DMARC checks.
By implementing DKIM and DMARC, you can protect your domain from spoofing, phishing, and spam while improving email deliverability, sender’s reputation, and overall credibility.
Why should I use DMARC?
Because DMARC provides a more robust and flexible way to validate the identity and integrity of the sender and email content based on the results of SPF and DKIM checks, using DMARC policy, you can define how the receiving email servers should handle email messages that fail DMARC checks, such as reject, quarantine, or none.
Also, you can request aggregate and forensic reports on your DMARC results from the receiving email servers for better performance and troubleshooting any issues or errors on time.
What type of DNS is DKIM?
DKIM is a type of DNS TXT record that contains your domain’s public key, which the receiving email server uses to validate your email’s digital signature. The DKIM record also contains other tags and values that define how your DKIM record works, such as the key type, the hash algorithm, the service type, and the flags.
Can a domain have 2 DKIM records?
Yes, a domain can have two or more DKIM records as long as they use different selectors. A selector is a name that identifies a DKIM record. For example, you can use “default” as one selector and “backup” as another selector for two different DKIM records. The format of the TXT record name for a DKIM record is selector._domainkey.domain, where selector is your chosen selector and domain is your domain name.
Do you need DKIM for DMARC?
In short, the answer is YES; you need DKIM for DMARC because DMARC relies on both SPF and DKIM checks to validate the sender and content authentication. If you only have SPF but not DKIM, then your email messages may fail DMARC checks if the receiving email servers modify or alter your email content in any way, such as adding a footer or changing the encoding.
Does DMARC encrypt email?
No, DMARC does not encrypt email. If you want to encrypt your email content, you need to use other methods such as S/MIME or PGP, which use public key cryptography to encrypt and decrypt your email content with a pair of keys: a public key that you share with your recipients, and a private key that you keep secret in your email header.
Is DMARC the same as DKIM and SPF combined?
No, DMARC is not the same as DKIM and SPF combined. DMARC relies on SPF and DKIM. It also enhances and extends SPF and DKIM with additional features and functions that make them more powerful and effective for validating the identity of the sender and content identity.


 OpenAI
OpenAI Perplexity
Perplexity

